What is better Linux or Windows?
Window VS Linux
Windows is a popular and widely used family of graphical operating systems developed by Microsoft. It provides a user-friendly interface for interacting with and managing computer hardware, software, and files. Windows-based operating systems offer a range of features and functionalities that enable users to perform tasks, run applications, and access a variety of resources on their computers. The term "Windows" is often used to refer to a specific version of the Microsoft Windows operating system, such as Windows 10, Windows 11, or earlier editions, each of which may have distinct features and improvements.
Linux is a type of computer operating system, like Windows or macOS, but it's free and open-source. It's used to control and manage a computer's hardware and software, making it work effectively. Linux is known for its stability, security, and flexibility, and it's widely used in servers, smartphones, and many other devices. It's created and maintained by a global community of developers who collaborate to improve and share it with anyone who wants to use it.
Features of windows:
Multitasking Capabilities: Windows allows users to run multiple applications simultaneously, making it easy to switch between tasks and increase productivity.
File Management: Windows offers efficient tools for creating, organizing, and managing files and folders, simplifying data management.
Software Compatibility: Windows is compatible with a wide range of software applications, including productivity tools, games, and specialized software, ensuring versatility and access to a broad software ecosystem.
Internet Connectivity and Browsing: Windows includes built-in internet connectivity features, such as web browsers, networking tools, and Wi-Fi management, enabling users to easily access the internet.
Security Features: Windows provides a range of security features, including user account controls, Windows Defender (built-in antivirus), and regular security updates to protect against threats.
Windows Update: Microsoft regularly releases updates to enhance performance, fix issues, and improve security, ensuring that the operating system remains up to date and secure.
Features of linux:
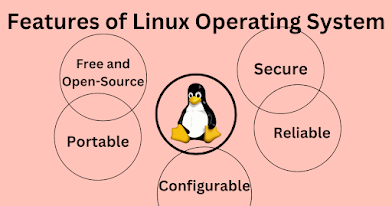
Open Source and Free: Linux is open-source, meaning the source code is freely available, and it can be modified and distributed by anyone. This fosters a vibrant community of developers and users who collaborate to improve the system. Most Linux distributions are also free to use, making it a cost-effective choice.
Stability and Reliability: Linux is known for its stability and reliability. It is often used in critical environments, such as servers, where uptime is essential. Linux systems can run for extended periods without needing to be restarted.
Security: Linux is recognized for its robust security features. The open-source nature of the operating system allows for continuous security improvements, and Linux has a reputation for being less susceptible to malware and viruses compared to other operating systems.
Customization: Linux is highly customizable, allowing users to tailor the operating system to their specific needs. Users can choose from a wide variety of desktop environments, software packages, and configurations to create a personalized computing environment.
Multitasking and Multiuser: Linux supports multitasking, enabling users to run multiple applications simultaneously. It also supports multiuser environments, allowing multiple users to work on the same system with their own user accounts and permissions.
Command Line Interface (CLI): Linux provides a powerful command-line interface (CLI) that allows users to perform advanced system tasks and automation. This is favored by system administrators and developers for its flexibility and efficiency.
Wide Hardware Support: Linux has extensive hardware support, and it can run on a wide range of hardware platforms, from personal computers to embedded systems and servers. This flexibility makes it suitable for various use cases.
window vs linux

User Interface:
Windows: Windows is known for its user-friendly graphical user interface (GUI). It provides an intuitive experience with icons, windows, and menus, making it accessible to a wide range of users.
Linux: Linux offers a variety of desktop environments, such as GNOME, KDE, and Xfce, which provide graphical interfaces similar to Windows. However, it also allows users to work entirely from the command line if desired.
Software Compatibility:
Windows: Windows has a vast library of software and applications developed for it, including popular commercial software like Microsoft Office and Adobe products.
Linux: While Linux has a rich ecosystem of open-source software, some commercial software is not available for Linux. However, many alternatives and open-source equivalents exist for various applications.
Cost:
Windows: Windows is a commercial operating system, and users typically need to purchase licenses. There are also free versions like Windows 10 Home, but these often come with certain limitations.
Linux: Linux is open source and typically free of cost. Users can choose from a wide range of Linux distributions (distros), each with its own characteristics and support models.
Security:
Windows: Windows has improved its security features over the years, including built-in antivirus (Windows Defender) and regular security updates. However, it remains a common target for malware and viruses due to its widespread use.
Linux: Linux is known for its strong security features, largely due to its open-source nature and user privileges system. Vulnerabilities are typically patched quickly, and it is less prone to malware.
Flexibility:
Windows: Windows is designed for general-purpose use, making it suitable for desktops, laptops, and a wide range of applications. It's less flexible when it comes to customizing the core of the operating system.
Linux: Linux is highly customizable. Users can tailor the OS to their specific needs, making it suitable for a broader range of applications, including servers, embedded systems, and supercomputers.
Community and Support:
Windows: Microsoft offers official support for Windows, and there is a large user community. Commercial support is available for enterprises.
Linux: Linux has a strong and supportive open-source community. Users can seek help from forums, online resources, and dedicated communities. Commercial support is also available through various vendors.
Hardware Support:
Windows: Windows has wide hardware support and is often the default OS for consumer desktops and laptops.
Linux: Linux also offers extensive hardware support and can run on various hardware platforms, including older and resource-constrained systems.

In conclusion, the choice between Windows and Linux as an operating system depends on several factors, including the user's needs, preferences, and specific use cases. Each has its own set of strengths and weaknesses:
Windows offers a user-friendly graphical interface, extensive software compatibility, and widespread commercial software support. It's commonly used on desktops and laptops, making it a preferred choice for everyday users, gamers, and businesses. However, it comes with licensing costs and may be more susceptible to security threats.
Linux, being open source, offers cost-free alternatives with high levels of stability, security, and flexibility. It's favored for server environments, embedded systems, and development purposes. The variety of distributions allows users to choose the one that aligns with their requirements, but it may require a steeper learning curve, especially for those accustomed to Windows.






Post a Comment
0 Comments