Learn about technologies scam
SCAM
A scam is a fraudulent or deceptive scheme or operation designed to deceive and manipulate individuals or organizations for financial gain or to obtain valuable information. Scams are often carried out by individuals or groups with dishonest intentions, and they use various methods to trick people into giving up money, personal information, or other resources.

Scams can take many forms and are conducted through various channels, including online, over the phone, through email, in person, or via traditional mail. Common characteristics of scams include false promises, misleading information, and a hidden agenda to defraud or harm the victim
Phishing Scams:
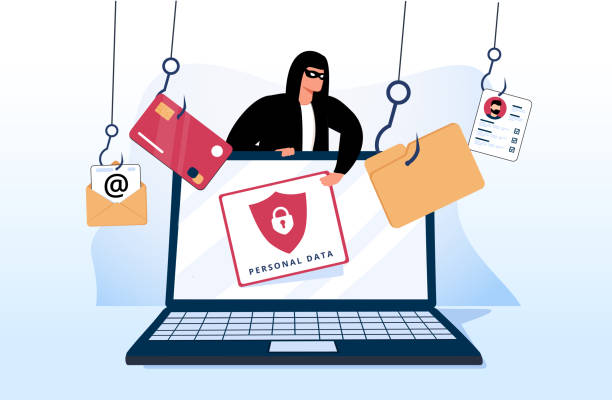

Phishing scams are fraudulent attempts to trick people into revealing their personal or sensitive information, such as passwords, credit card numbers, or social security numbers. The term "phishing" is a play on the word "fishing," as scammers are essentially fishing for your valuable information.
Email Phishing:
Example: You receive an email that appears to be from your bank, asking you to click on a link and log in to your account to verify your information. The email looks real, but it's actually from a scammer trying to steal your login credentials.
How to Spot: Check the email address of the sender, and be cautious of urgent requests for personal information. Real banks typically don't ask for sensitive information via email.
Social Media Phishing:
Example: You receive a message on a social media platform from someone posing as a friend. They ask you to click on a link and enter your login credentials to access a supposed funny video. In reality, it's a scam to steal your social media account details.
How to Spot: Verify the identity of the sender. If the message seems unusual or requests sensitive information, be cautious.
Website Phishing:
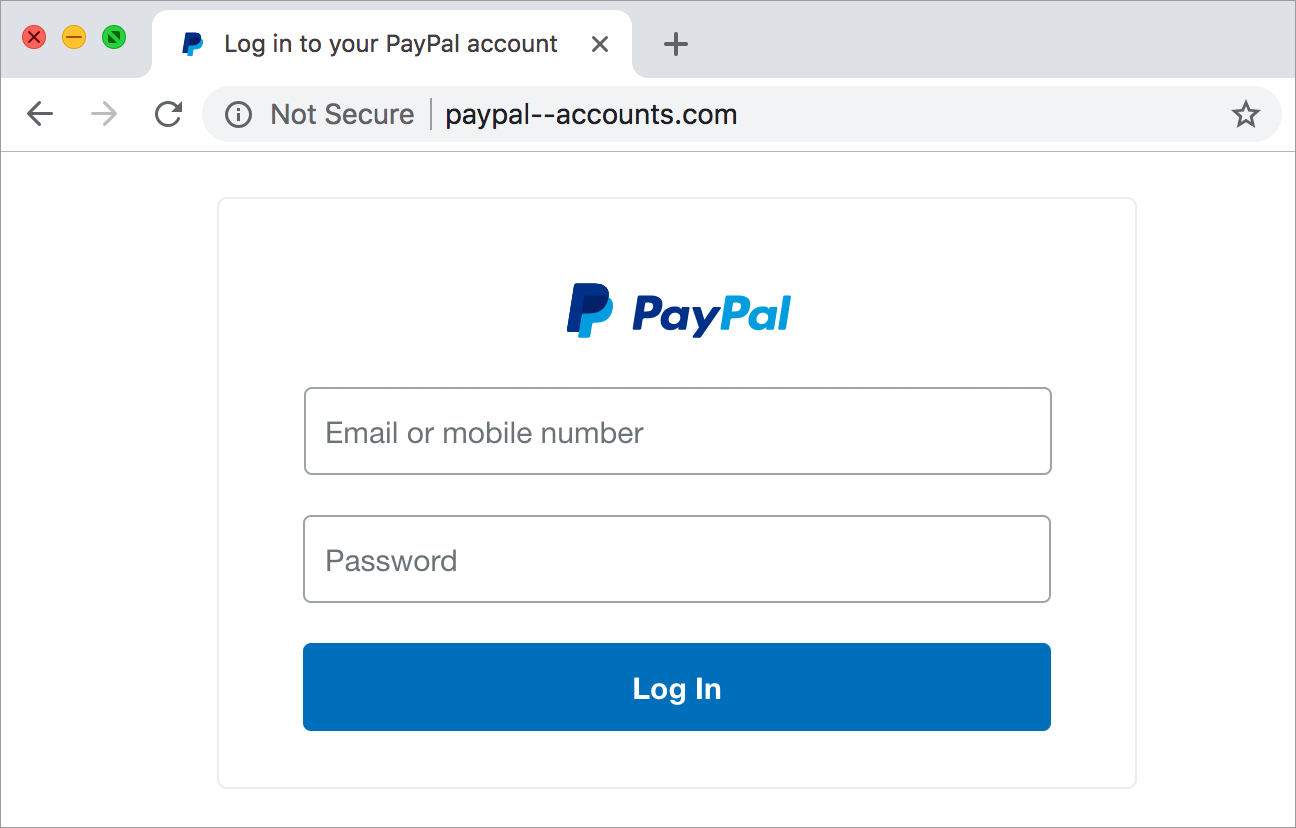 |
Example: You land on a website that looks like an official login page for an online service, like an email or banking website. You enter your username and password, but the site is a fake one created by scammers to steal your login details.
How to Spot: Always double-check the web address in your browser's address bar. Make sure it matches the official website's domain.
Online Auction and Sales Scams
Online auction and sales scams are schemes where fraudsters attempt to deceive people during online transactions, often involving buying or selling items. The scammers aim to take money or goods without delivering what was promised.
To avoid online auction and sales scams:

Be skeptical of deals that seem too good to be true: If a product is significantly cheaper than the market price, it may be a red flag.
Use secure payment methods: Whenever possible, use payment methods that offer buyer protection, such as PayPal or credit cards. Avoid wire transfers or gift cards, as they offer little recourse for recovering lost funds.
Research the seller: Look at the seller's history, reviews, and ratings on the online marketplace. Scammers often have little or no positive feedback.
Meet in person for high-value items: If buying a valuable item, consider meeting the seller in a public place to inspect the product before making payment.
Beware of urgency and personal stories: Scammers often create a sense of urgency and invent personal stories to manipulate your emotions. Take your time and don't rush into a purchase.
Ransomeware
Ransomware is a type of malicious software that hackers use to lock your computer or files and demand money (a "ransom") in exchange for unlocking them. It's like a digital kidnapper holding your data hostage.
To protect against ransomware:

Backup your data: Regularly back up your important files to an external drive or cloud storage. This way, you can restore your data if it's ever encrypted by ransomware.
Be cautious of email attachments and links: Ransomware often spreads through malicious email attachments or links. Don't open attachments or click on links from unknown or suspicious sources.
Use reputable security software: Install and regularly update antivirus and anti-malware software to detect and prevent ransomware infections.
Keep your operating system and software up to date: Security updates often fix vulnerabilities that ransomware exploits to infect your computer.
Don't pay the ransom: It's generally discouraged to pay ransom demands. Instead, report the incident to law enforcement and seek professional assistance to remove the ransomware.
Cybersecurity and Scam Prevention

Cybersecurity is like a digital shield that protects your computer and online information from bad actors who want to steal, damage, or misuse your data. It's the armor for your online world.
Scam prevention means taking steps to avoid falling for tricks or deceitful schemes that aim to harm you or steal your information, like your passwords or money.
Example: Protecting Your Passwords
Think of your online accounts, like email or social media, as treasure chests. Your password is the key to these chests.
Cybersecurity means using strong, unique keys (passwords) that are hard for others to guess. For instance, "P@ssw0rd123" is stronger than "password123."
Scam prevention involves not sharing your key (password) with anyone who asks, especially if they claim to be from a company or a website.
If you receive an email or message asking for your password, even if it looks official, it might be a scam. Cybersecurity means not falling for it and reporting it to the real company.
Impact of Scams on Individuals and Businesses
The impact of scams on individuals and businesses can be substantial, resulting in financial losses, damaged reputations, and emotional distress. Here's an explanation with an example:
Individual Impact:
Financial Loss:
Example: An individual receives a phone call from a scammer claiming to be from the IRS, stating that they owe back taxes and must pay immediately to avoid arrest. The victim pays a large sum of money, only to later realize it was a scam. This leads to a significant financial loss.
Emotional Distress:
Example: A person falls victim to an online romance scam, developing a close relationship with someone they met on a dating website who later asks for money. When the scam is revealed, the victim experiences emotional trauma and distress.
Identity Theft:
Example: An individual receives a phishing email that appears to be from their bank, and they unwittingly provide their login credentials. Scammers access the victim's bank account, causing financial turmoil and potential long-term identity theft issues.
Business Impact:
Financial Loss:
Example: A small business owner falls victim to a business email compromise (BEC) scam where the scammer impersonates a trusted supplier and redirects payment for a large order to the scammer's account. The business suffers a substantial financial loss.
Reputation Damage:
Example: A data breach at a healthcare facility results in the exposure of patient records, leading to a loss of patient trust and potential legal consequences, which can harm the facility's reputation.
Operational Disruption:
Example: A manufacturing company's computer systems are infected with ransomware, which encrypts critical production data. The company must pay a ransom to recover its data or face prolonged operational disruption, causing financial losses.
The Role of Machine Learning in Scam Detection

Machine learning in scam detection is like having a smart detective that learns from past experiences to catch new types of scams. It's a computer program that gets better at spotting tricks and frauds as it sees more of them.
Here's a simple explanation of the role of machine learning in scam detection:
Learning from Data: Imagine a computer program that looks at lots of data, like emails, transactions, or website activity. It learns patterns from this data, such as what normal or typical behavior looks like.
Spotting Anomalies: When new data comes in, the program can compare it to what it's learned. If the new data looks different or suspicious, it raises a flag, like a detective noticing something unusual.
Adapting Over Time: The more data the program sees, the better it becomes at detecting scams. It learns from its mistakes and successes, just like a detective gets better at solving cases with more experience.
Real-Time Protection: Machine learning can work quickly and in real-time. It's like having an instant detective that can warn you about potential scams, whether it's a phishing email or a suspicious transaction.
The Dark Web and Scam Marketplaces

The Dark Web is like a hidden part of the internet, where websites and services are not indexed by search engines. It's often used for privacy and secrecy, but it can also be a place where illegal activities, including scam marketplaces, happen.
Here's a simple explanation of the Dark Web and scam marketplaces:
The Hidden Internet: Imagine the internet as an iceberg. The top, visible part is the regular internet you use every day. The hidden, underwater part is the Dark Web. You can't find Dark Web websites using regular search engines like Google.
Secrecy and Anonymity: People use the Dark Web for privacy and anonymity. It's a place where users and websites can hide their identity and activities.
Scam Marketplaces: Unfortunately, the Dark Web is also a place where illegal things can be bought and sold. This includes scams, stolen data, counterfeit money, hacking tools, and more. Scammers use it to exchange information and tools for their fraudulent activities.

In conclusion, scams are deceptive and fraudulent schemes designed to exploit individuals, organizations, and even governments for financial gain or to steal valuable information. They come in various forms, from phishing emails and tech support scams to online auction fraud and investment schemes. Scammers use a combination of psychology, technology, and manipulation to lure their victims.











Post a Comment
0 Comments