how to know website
The World Wide Web, often abbreviated as the "web," is a fundamental and integral part of the internet that has revolutionized the way we access and share information. In simple terms, the web can be thought of as a vast, interconnected collection of digital pages, resources, and content that can be accessed through web browsers.

At its core, the web is a global network of information that spans the entire world. It's made up of billions of individual web pages, websites, and digital assets, all hosted on servers and accessible via the internet. These pages and websites are created by people, organizations, and businesses, and they cover a wide range of topics and interests, from news and entertainment to education and e-commerce.
Types of Web
Informational Websites:
An online encyclopedia providing information on a wide range of topics.
E-commerce Websites:
eBay (www.ebay.com):
An online auction and shopping website.
Social Media Platforms:
Facebook (www.facebook.com):
A social networking platform for connecting with friends and sharing content.
Instagram (www.instagram.com):
A platform for sharing photos and short videos.
Blogs:
A platform for writers to publish articles and stories on various topics.
A blog focused on technology news and analysis.
Portfolio Websites:
Behance (www.behance.net):
A platform for creative professionals to showcase their design portfolios.
Dribbble (dribbble.com):
A community of designers showcasing their work.
Web Trends and Future Predictions
5G Technology and the Web:
Web Browsing:
With 5G, web pages load almost instantly, offering a smoother and more efficient browsing experience. Users can access data-intensive websites with rich multimedia content without delays. For example, image-heavy websites or online marketplaces can load quickly, enhancing the user experience.
Web Development:
Web developers will need to adapt to 5G's capabilities. Mobile-first web design, responsive layouts, and optimized content for faster loading times will be crucial. Web developers can create web apps that make full use of 5G's potential, such as real-time collaborative tools or advanced multimedia experiences.
Web Gaming:

Cloud gaming, where games are streamed from servers to players' devices, will benefit greatly from 5G. Services like Google Stadia or NVIDIA GeForce Now leverage 5G for low-latency, high-quality gaming experiences. Gamers can access console-level gaming through web browsers on their devices.
Streaming:

5G is a game-changer for video streaming services. Users can stream 4K and even 8K videos seamlessly. Streaming platforms like Netflix and YouTube can deliver high-quality content without buffering, providing a more enjoyable viewing experience.
The Future of Web Development
Advanced User Experiences:
Web development will focus on creating highly immersive and interactive user experiences. This includes integrating technologies like augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) to offer engaging and visually compelling web applications.
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs):
PWAs will continue to gain popularity, providing fast, reliable, and app-like experiences on the web. They will be a standard approach for developing web applications that work seamlessly on various devices.
WebAssembly (Wasm):
WebAssembly will revolutionize web development by allowing high-performance applications to run directly in web browsers. This technology will enable developers to build web apps with near-native speed and functionality.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning:
AI and machine learning will become integral to web development, improving personalization, chatbots, data analysis, and content recommendation. AI-driven web applications will enhance user engagement and efficiency.
Voice and Conversational Interfaces:
Voice-activated search, virtual assistants, and chatbots will become more sophisticated, offering web users the convenience of natural language interactions. Voice commerce (v-commerce) will grow in significance.
Green Web Development:
Sustainability will become a central concern, leading to the development of eco-friendly web applications and practices to reduce the environmental footprint of digital technologies.
Quantum Computing:
As quantum computing advances, web developers may leverage this technology for complex calculations, data encryption, and solving problems that are currently beyond the capabilities of classical computers.
Web Security and Privacy: Safeguarding the Digital World
Web Security:
Definition: Web security encompasses measures and practices to protect websites, web applications, and web users from cyber threats and vulnerabilities.
Examples:
HTTPS Encryption: Implementing HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) ensures data transmitted between the user's browser and the web server is encrypted. For example, when you visit your online banking website, you'll notice a padlock icon in the address bar, indicating a secure connection.
Web Privacy:
Definition: Web privacy refers to the protection of an individual's personal data and online activities from unauthorized access and misuse.
Examples:
Data Protection Regulations: Privacy regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States mandate how organizations handle user data. Violations can lead to substantial fines. For instance, Google was fined €50 million for GDPR non-compliance.
Cybersecurity Threats:

Definition: Cybersecurity threats are risks and vulnerabilities that can compromise web security and privacy.
Examples:
Phishing Attacks: Cybercriminals use fraudulent emails or websites that mimic legitimate organizations to steal personal information. For instance, a user receives an email purportedly from their bank, asking them to update their login credentials on a fake website.
Importance of End-to-End Encryption:
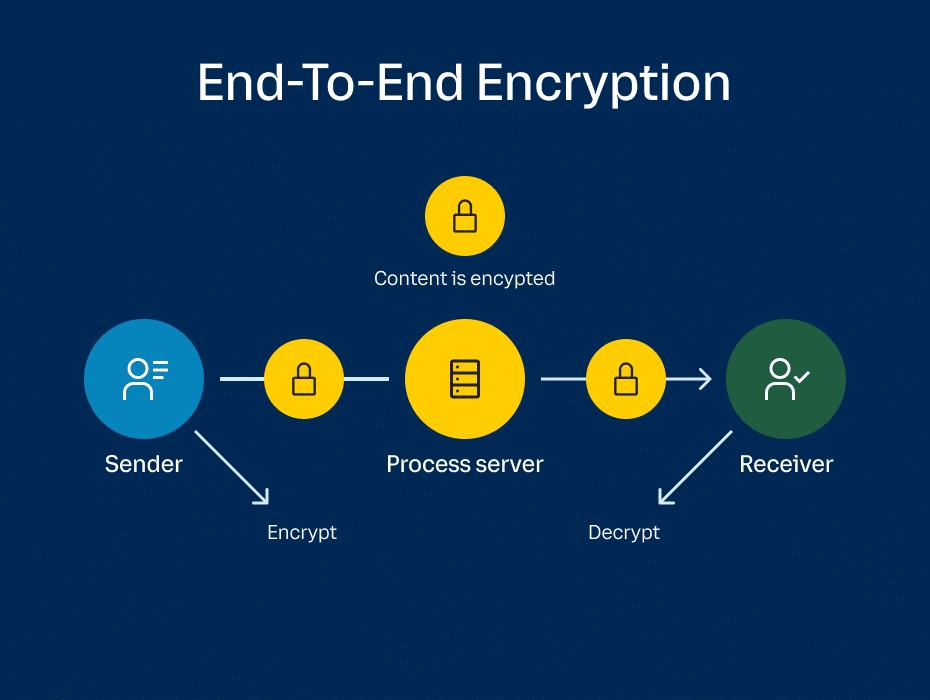
Definition: End-to-end encryption (E2E) ensures that only the sender and the recipient of a message can access its contents.
Example: Messaging apps like Signal and WhatsApp use E2E encryption to secure user communications. Even the service providers cannot access the content of messages, enhancing user privacy.
How Web works?
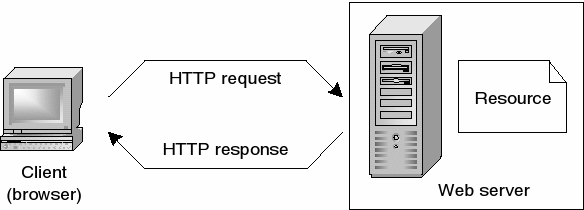
Client-Server Architecture:
The web operates on a client-server model. Clients, such as web browsers (e.g., Chrome, Firefox), request web content, while servers store, process, and deliver that content.
Domain Name System (DNS):
When you enter a web address (e.g., www.example.com) into your browser, the DNS system translates this human-readable domain name into an IP address, which is a unique numerical identifier for the server hosting the website.
HTTP/HTTPS Requests:
Once the browser has the server's IP address, it sends an HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) or HTTPS (HTTP Secure) request to the server to retrieve the web page.
Server Processing:
The server receives the request and processes it. It may interact with databases, perform calculations, and generate dynamic content, depending on the type of website or web application.
Web Page Generation:
The server assembles the web page by combining the requested content, such as HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) for structure, CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) for presentation, and JavaScript for interactivity. This content is generated dynamically for database-driven websites.
HTTPS Encryption:
For secure websites (using HTTPS), data exchanged between the client and server is encrypted to protect it from interception or tampering. This is crucial for online security and privacy.
Server Response:
The server responds to the client's request by sending back the web page along with HTTP status codes (e.g., 200 for a successful request, 404 for a not found page).
Rendering the Web Page:
The web browser receives the response and interprets the HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to render the web page on the user's screen. The browser also makes additional requests for resources like images, stylesheets, and scripts.
Caching:
To improve performance, web browsers and servers use caching. The browser stores some web content (e.g., images) locally, reducing the need to request the same resources from the server every time a user visits a site.
User Interaction:
Users can interact with the web page by clicking links, submitting forms, and performing various actions. These interactions trigger new HTTP requests to the server, resulting in dynamic responses.
Cookies and Session Management:

Cookies are small pieces of data sent from the server and stored on the user's device. They help maintain stateful interactions, such as keeping a user logged in or remembering their preferences during a session.
Web Applications:
Some websites are dynamic web applications that process user inputs and return results, often without the need to reload the entire page. JavaScript frameworks and libraries like React, Angular, and Vue.js enable these interactive experiences.
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces):
Many web services and applications provide APIs that allow other programs or websites to request and exchange data. This facilitates integration and data sharing across different platforms.
Web Security:
Security measures like HTTPS, firewalls, and secure coding practices protect web users and their data from cyber threats. Firewalls can filter out malicious traffic, while secure coding helps prevent vulnerabilities that could be exploited.
Web Standards and Protocols:
The web relies on a variety of standards and protocols, such as HTTP/HTTPS, HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and more. These ensure consistency, compatibility, and the ability for different browsers and servers to communicate effectively.
In conclusion, the web is a dynamic and ever-evolving ecosystem that has fundamentally transformed the way we connect, communicate, and access information in the digital age. From its humble origins as a text-based platform, the web has evolved into a rich and diverse landscape, underpinned by a multitude of technologies and protocols.





Post a Comment
0 Comments